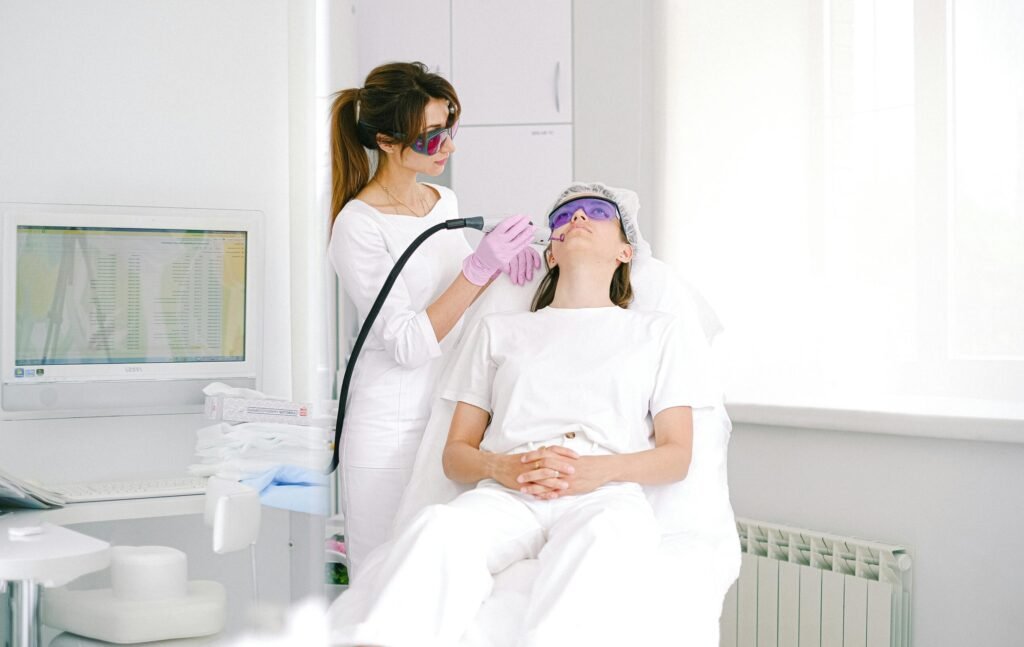
Types of Lasers and How They Work
Lasers have become a cornerstone of modern dermatology and aesthetic medicine, offering non-invasive and effective solutions to a wide range of skin concerns, from scars to unwanted hair. The word “laser” stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation—a process that focuses light into a concentrated beam of energy. Depending on the laser’s wavelength and power, it can interact with different layers of the skin for various treatments. Understanding the types of lasers and how they work is key to knowing which is best suited for your specific skin concerns.
How Lasers Work
Laser devices emit a concentrated beam of light at a specific wavelength, which interacts with the skin in a targeted manner. Different skin components, like water, melanin (the pigment responsible for skin color), or hemoglobin (found in blood vessels), absorb certain wavelengths of light. By using the appropriate wavelength, lasers can focus on these targets without affecting the surrounding tissue.
Lasers are primarily classified into two categories based on how they interact with the skin:
- Ablative Lasers: These lasers vaporize the outer layers of the skin, promoting new skin growth and collagen production. Ablative lasers are ideal for deeper wrinkles, scars, and extensive skin resurfacing.
- Non-Ablative Lasers: These lasers work beneath the surface of the skin without removing the top layer. They target issues like pigmentation, fine lines, and vascular lesions while promoting collagen remodeling over time.
Let’s explore some of the most commonly used lasers and their functions in dermatology.
1. CO2 Lasers (Carbon Dioxide Lasers)
- How they work: CO2 lasers are ablative lasers that emit a high-energy beam of infrared light at a wavelength of 10,600 nm. They vaporize the outer layers of damaged skin, stimulating collagen production and revealing smoother, healthier skin beneath. CO2 lasers are known for their precision and ability to target deep skin issues.
- What they treat: CO2 lasers are highly effective for deep wrinkles, acne scars, warts, skin tags, and sun-damaged skin. They can also be used for skin resurfacing and tightening.
- Recovery time: Since CO2 lasers are ablative, recovery can take 1-2 weeks, during which time patients may experience redness, swelling, and peeling.
2. Erbium (Er:YAG) Lasers
- How they work: Erbium lasers are another type of ablative laser, but they emit light at a wavelength of 2,940 nm, which is specifically absorbed by water in the skin cells. This makes Er:YAG lasers highly precise, vaporizing the skin with minimal thermal damage to surrounding tissues compared to CO2 lasers.
- What they treat: These lasers are often used for moderate wrinkles, fine lines, age spots, and superficial skin resurfacing. They’re also ideal for treating skin with less pigmentation or sensitivity to heat.
- Recovery time: Recovery with Erbium lasers is generally faster than with CO2 lasers, usually taking about 5-7 days. There is less risk of hyperpigmentation, making it more suitable for individuals with darker skin tones.
3. Nd:YAG Lasers
- How they work: Nd:YAG lasers emit light at a wavelength of 1,064 nm, which is absorbed by hemoglobin and melanin. This non-ablative laser penetrates deeply into the skin and is ideal for treating vascular conditions and pigmentation issues without damaging the skin’s surface.
- What they treat: Nd:YAG lasers are commonly used for hair removal, treating spider veins, reducing redness, and targeting deeper pigmentation concerns. They are also effective for tattoo removal and skin rejuvenation.
- Recovery time: Since Nd:YAG lasers are non-ablative, recovery time is minimal, and side effects are generally limited to mild redness or swelling.
4. Pulsed Dye Lasers (PDL)
- How they work: Pulsed dye lasers work by emitting a concentrated beam of light at a wavelength of 585-595 nm, which is absorbed by the blood vessels. These lasers convert the light energy into heat, destroying the targeted blood vessels without damaging the surrounding tissue.
- What they treat: PDLs are primarily used to treat vascular conditions such as rosacea, spider veins, port-wine stains, and redness. They are also effective in treating hypertrophic scars and some forms of hyperpigmentation.
- Recovery time: Side effects can include temporary redness or bruising, but recovery is typically quick, with minimal downtime required.
5. Alexandrite Lasers
- How they work: Alexandrite lasers emit light at a wavelength of 755 nm, which is absorbed by melanin in the skin. This makes them ideal for targeting pigmentation issues and hair follicles for hair removal.
- What they treat: Alexandrite lasers are primarily used for hair removal on individuals with light to olive skin tones. They are also effective in treating age spots, freckles, and pigmented lesions.
- Recovery time: Recovery is minimal, with mild redness or swelling that subsides within a few hours to days. Alexandrite lasers are generally not recommended for people with darker skin tones due to the risk of hyperpigmentation.
6. Diode Lasers
- How they work: Diode lasers emit light at wavelengths ranging from 800-810 nm, targeting melanin in the hair follicles. They penetrate deep into the skin, making them highly effective for hair removal.
- What they treat: Diode lasers are commonly used for long-term hair reduction and are suitable for most skin types, including darker skin tones.
- Recovery time: Diode lasers typically have minimal side effects, with some mild redness or swelling that resolves quickly.
7. Fractional Lasers
- How they work: Fractional lasers, both ablative and non-ablative, create tiny columns of thermal damage in the skin while leaving the surrounding tissue intact. This allows the skin to heal faster than traditional ablative lasers while promoting collagen production and skin rejuvenation.
- What they treat: Fractional lasers are used to treat fine lines, wrinkles, acne scars, and stretch marks. They are ideal for individuals looking for moderate skin resurfacing with less downtime.
- Recovery time: Recovery depends on whether the fractional laser is ablative or non-ablative. Non-ablative fractional lasers typically require little downtime, while ablative versions may require up to a week for full recovery.
8. Ruby Lasers
- How they work: Ruby lasers emit light at a wavelength of 694 nm, which is highly absorbed by melanin. This makes them effective for treating pigmented lesions and for laser hair removal in light-skinned individuals.
- What they treat: Ruby lasers are used for hair removal, sunspots, and freckles. However, they are not recommended for darker skin tones due to the risk of pigmentation changes.
- Recovery time: Recovery from ruby laser treatments is generally mild, with temporary redness or swelling that subsides within a few days.
Conclusion
Laser technology offers a diverse range of treatments for various skin concerns, from pigmentation issues and vascular conditions to hair removal and skin resurfacing. The type of laser used in a treatment depends on the individual’s skin type, the condition being treated, and the desired results. While some lasers are more invasive and require longer recovery times, others offer effective treatments with minimal downtime. Consulting with a board-certified dermatologist is essential to determining the right laser for your skin needs and ensuring the best outcome.
To consult with our Doctors, email us at : info@unifiedastra.com